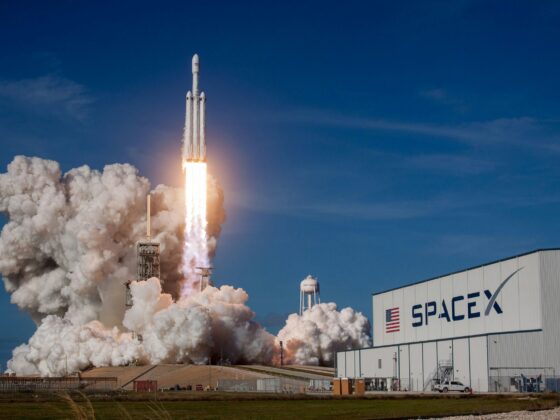
History was made. Intuitive Machines (IM-1) launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, marking the first flight of a commercially built lander to the Moon as part of NASA’s Artemis program. This mission signifies a crucial step forward in lunar exploration, leveraging private partnerships and innovative technology. Let’s take a look at what NASA Intuitive Machines-1 are:
The Nova-C Lander
The star of the show is “Odysseus,” a hexagonal behemoth standing 4 meters tall and carrying 1908 kg of cargo. Furthermore, Equipped with solar panels and capable of carrying 100 kg of payload, this Nova-C lander embodies the spirit of exploration and scientific discovery.
Science on Board: Unlocking Lunar Secrets
Odysseus carries five NASA payloads designed to unravel lunar mysteries. These include:
- Studies of plume-surface interactions: Observing how rocket exhaust interacts with the lunar surface, crucial for future moon landings.
- Space weather/lunar surface interactions: Investigating how charged particles from the Sun affect the lunar surface.
- Radio astronomy: Utilizing the Moon’s radio silence to make observations of the universe unobstructed by Earth’s noise.
- Precision landing technologies: Testing and refining techniques for future, more precise lunar landings.
- Communication and navigation node: Demonstrating potential technologies too for future autonomous navigation on the Moon.
Further, these experiments hold immense potential for advancing our understanding of the Moon, its resources, and its interactions with space.
Partnership Power
Furthermore, NASA Intuitive Machines-1 is a prime example of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, leveraging commercial partnerships to achieve lunar exploration goals. Further, this approach fosters innovation, reduces costs, and expands opportunities for diverse players in the space industry.
The Journey Unfolds: Anticipation for Landing
Besides, As of today, February 20th, 2024, Odysseus is on its multi-day journey to the Moon. Landing is targeted for February 22nd near the lunar South Pole, where it will embark on its scientific mission.